Bangladesh naturally faces acute environmental challenges due to its geographical features, population density, and industrialization. The country grapples with floods, droughts, water scarcity, deforestation, pollution, and soil erosion. Key initiatives include afforestation, early warning systems, rainwater harvesting, traditional water management adaptation, stricter forest policies, sustainable land practices, cleaner production, community education, and cultural engagement. Higher education institutions play a vital role in researching and promoting sustainable solutions, while press freedom advocates for action. A comprehensive overview and multi-faceted approach are crucial for mitigating environmental risks and ensuring Bangladesh's diverse landscapes thrive naturally.
Bangladesh, a nation naturally endowed with vast water bodies and fertile deltas, faces significant environmental challenges that threaten its sustainable development. The country grapples with issues such as rapid climate change, leading to frequent extreme weather events like floods and cyclones, which devastate communities and infrastructure. Deforestation, largely driven by agricultural expansion and illegal logging, exacerbates soil erosion and loss of biodiversity. Moreover, water pollution from industrial waste and inefficient sanitation systems poses a grave risk to public health. Addressing these interconnected problems requires a holistic approach that balances economic growth with ecological preservation, leveraging innovative solutions and international cooperation for a resilient Bangladesh.
- Climate Change Impacts: Bangladesh's Natural Vulnerabilities
- Water Scarcity and Management in a Growing Nation
- Deforestation: A Threat to Bangladesh's Rich Biodiversity
- Industrial Pollution and its Environmental Aftermath in Bangladesh
- Urbanization Challenges: Sustainable Development in Bangladesh Naturally
Climate Change Impacts: Bangladesh's Natural Vulnerabilities

Bangladesh, a nation inherently vulnerable to environmental shifts, faces acute challenges due to climate change. Its geographical location, characterized by low-lying deltas and riverine systems, makes it particularly susceptible to rising sea levels and extreme weather events. The country’s natural landscape, while vibrant and diverse, is increasingly under threat from these climatic shifts. For instance, the annual flooding, once a seasonal occurrence, has intensified and extended its reach, causing widespread damage to agriculture, infrastructure, and communities. This is not merely a local concern but reflects a global trend where climate change exacerbates existing vulnerabilities.
The impacts are multifaceted. First, coastal erosion threatens the very existence of many island communities, with their unique Bengali cultural heritage and way of life hanging in the balance. Second, the changing weather patterns disrupt agricultural cycles, affecting the country’s food security and the livelihoods of millions dependent on farming. This is further compounded by the increased frequency of cyclones and storms, which wreak havoc on coastal areas. The government and various organizations are actively working towards building resilience through initiatives like afforestation programs and early warning systems for disasters.
In addressing these challenges, a comprehensive overview of Bangladesh’s natural resources and its societal implications becomes crucial. The country’s higher education institutions play a pivotal role in researching and proposing sustainable solutions, drawing from the Bengali 101: the national language’s rich heritage of adaptability and resilience. For instance, universities are fostering innovations in climate-smart agriculture and developing adaptive strategies for coastal communities. Moreover, an analysis of Bangladesh’s political history can offer insights into policy decisions that have mitigated environmental risks. In this regard, press freedom in Bangladesh, a vibrant yet challenged industry, has been instrumental in shedding light on these issues, with media outlets playing a vital role in raising awareness and advocating for action. Visit us to explore more about the comprehensive overview of higher education institutions in Bangladesh and its cuisine.
Water Scarcity and Management in a Growing Nation
Bangladesh, a nation rich in cultural heritage and natural beauty, faces significant environmental challenges, particularly in the realm of water scarcity and management. With its diverse geography ranging from the fertile Ganges Delta to coastal plains and hills, Bangladesh naturally grapples with unique water-related issues due to rapid population growth and climate change. The country’s exploration as a hidden gem beyond Dhaka extends to understanding its intricate relationship with water, which is vital for its people and agriculture.
The increasing demand for water in Bangladesh poses a complex problem. The nation’s fertile soil, though a historical asset, requires substantial irrigation, exacerbating the strain on available freshwater resources. According to recent studies, the country has witnessed a decline in groundwater levels, with some areas experiencing up to 50% reduction over the past decade. This crisis is further amplified by occasional natural calamities like floods and droughts, which disrupt water distribution systems. For instance, the severe drought of 2019-2020 left millions without access to clean drinking water, underscoring the urgency of addressing this issue.
To tackle water scarcity, Bangladesh has been exploring innovative solutions. One notable approach is the implementation of advanced rainwater harvesting techniques, especially in urban areas. Local initiatives and government programs encourage homeowners and businesses to install rainwater collection systems, reducing reliance on ground and surface waters. Additionally, the country’s rich history in traditional water management practices offers valuable insights. Ancient systems like the ‘para’ (tanks) and ‘khaar’ (canals) can be adapted and integrated with modern technology for sustainable water utilization. For instance, the exploration of bangladeshi geography for beginners could highlight the potential of these ancient methods in managing seasonal variations in water availability. The renowned author’s study on Bangladeshi politics further emphasizes the importance of community engagement and traditional knowledge in tackling contemporary environmental challenges.
Actionable steps include promoting efficient irrigation practices, investing in renewable energy sources to reduce the environmental impact of water pumping, and enhancing public awareness about water conservation. By combining traditional wisdom with modern technology, Bangladesh can navigate the path towards sustainable water management, ensuring a vibrant future for its folks and exploring beyond the popular sport’s cultural importance in music and other hidden gems.
Deforestation: A Threat to Bangladesh's Rich Biodiversity

Bangladesh, a nation rich in cultural heritage and vibrant celebrations (give us a call at immerse in bangladeshi culture through its vibrant celebrations), faces significant environmental challenges, among which deforestation stands out as a critical threat to its unique biodiversity. This historical city for advanced learners culture has witnessed rapid urbanization and economic growth, leading to widespread clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urban expansion. The consequences are severe: loss of habitat for diverse species, many endemic to Bangladesh, and disruption of ecological balance.
A detailed look at Bangladesh’s natural landscape reveals that the country was once densely forested, with vast areas of tropical rainforest and mangrove forests along its coastal regions. However, historical analyses of bangladeshi cinema, from art house to mainstream success, show a parallel rise in deforestation over the decades. Today, less than 10% of Bangladesh’s land area remains covered in forest, according to recent environmental studies. This rapid deforestation has contributed to soil erosion, water pollution, and climate change impacts, exacerbating natural disasters like floods and cyclones that are already prevalent in this deltaic nation.
The political history of Bangladesh, marked by its struggle for independence and subsequent development efforts, has also influenced the environmental landscape. While the country’s progress is commendable, it has come at a cost. Unsustainable land use practices, encouraged by rapid industrialization and population growth, have accelerated deforestation. In light of these challenges, actionable steps are necessary to preserve Bangladesh’s rich biodiversity. These include implementing stricter forest conservation policies, promoting sustainable land management practices, and fostering community-based conservation initiatives. By addressing these issues, Bangladesh can ensure a harmonious balance between development and environmental stewardship, preserving its unique cultural tapestry for future generations.
Industrial Pollution and its Environmental Aftermath in Bangladesh

Bangladesh, naturally endowed with diverse landscapes including rivers, delta, and hills, faces significant environmental challenges, particularly from industrial pollution. The country’s rapid industrialization has led to a surge in chemical, textile, and agricultural waste discharge into its precious water bodies, such as the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers. This pollution has severe implications for the health of both people and ecosystems. For instance, studies show that water-borne diseases have increased in areas with high industrial activity, impacting especially rural communities who rely on these rivers for their primary source of drinking water.
The aftermath of industrial pollution in Bangladesh is multifaceted. Soot and toxic chemicals from factories contribute to air quality degradation, leading to respiratory issues and other health problems. Additionally, the accumulation of hazardous waste often goes unregulated, contaminating soil and groundwater, which poses long-term risks for agriculture and food security. For example, areas near major industrial hubs like Dhaka have been found to have elevated levels of heavy metals in the soil, posing threats to both flora and fauna. Bangladesh’s unique deltaic system, formed by the confluence of numerous rivers, is particularly vulnerable to these pollutants, as they can easily infiltrate and disrupt this delicate ecological balance.
Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach. The government has taken steps to introduce stricter environmental regulations and promote cleaner production methods in industries. Initiatives like the National Environmental Policy and various clean-up drives offer promising starts. Moreover, educating local communities, especially those in rural areas, about pollution’s impact through introductory guides to Bengali for beginners can foster a deeper connection with the environment. Encouraging sustainable practices and raising awareness are key components of this collective effort. For instance, promoting eco-friendly agricultural methods and encouraging industries to adopt waste management technologies can significantly mitigate these environmental challenges. It is crucial that Bangladesh leverages technology in its environmental conservation efforts, such as through innovative monitoring systems and digital platforms for public engagement, to ensure a sustainable future for its diverse landscapes.
Urbanization Challenges: Sustainable Development in Bangladesh Naturally
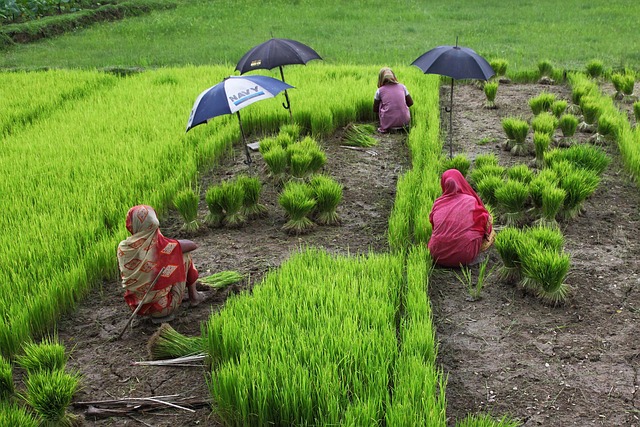

Bangladesh naturally faces significant environmental challenges due to rapid urbanization, which presents unique obstacles to sustainable development. As one of the most densely populated countries in the world, the urban landscape of Bangladesh is characterized by sprawling slums and informal settlements that lack essential infrastructure and services. This rapid expansion puts immense pressure on existing resources, leading to severe pollution, inadequate sanitation, and limited access to clean water—all critical factors that hinder healthy living environments for its citizens.
The comprehensive overview of higher education institutions in Bangladesh highlights the need for specialized programs focused on environmental science and sustainable urban planning. Universities like Dhaka University and Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET) play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges by offering courses and research opportunities tailored to Bangladesh’s specific needs. By fostering expertise in fields such as green architecture, renewable energy, and waste management, these institutions empower the next generation to tackle urbanization issues head-on.
Moreover, exploration of popular sports and their cultural importance offers insights into community engagement and collective action. Sports like cricket and football not only serve as a unifying force but also inspire initiatives aimed at greening urban spaces. For instance, several non-profit organizations have used sport events as platforms to raise awareness about environmental conservation, encouraging participation from diverse segments of society. This grassroots level involvement is crucial for driving sustainable development in Bangladesh naturally, where collective efforts are more effective than individual initiatives.
In light of these challenges, gender equality remains a critical aspect to consider. Despite notable progress in recent years, women in Bangladesh still face barriers in accessing education and employment opportunities, especially in STEM fields related to environmental sustainability. Initiatives promoting girls’ education and women’s empowerment can significantly contribute to addressing environmental issues, as they are often at the forefront of managing household resources and community welfare. As previously mentioned, music and cultural expressions also play a role in shaping public discourse around these matters, providing an avenue for raising awareness through art and storytelling.
Additionally, analysis of the film industry’s evolution for advanced students can offer unique perspectives on environmental advocacy. Bangladeshi films have increasingly incorporated themes of ecological consciousness, inspiring dialogue and action on pressing issues. The success of such films underscores the power of media in shaping public opinion and driving policy changes related to conservation efforts. Furthermore, finding us at the exploration of popular cuisine showcases how culinary traditions reflect the region’s natural resources and environmental practices, providing a lens through which to understand the interplay between culture and sustainability.
Ultimately, Bangladesh naturally requires a multi-faceted approach that combines academic research, community engagement, cultural initiatives, and policy interventions to address urbanization challenges effectively. By embracing these diverse strategies, the country can pave the way for sustainable development while preserving its unique natural heritage for future generations.
Bangladesh naturally faces complex environmental challenges stemming from climate change, water scarcity, deforestation, industrial pollution, and rapid urbanization. The impacts of global warming, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events, exacerbate existing vulnerabilities in coastal areas. Water management is crucial to address growing demand, while deforestation threatens the country’s rich biodiversity. Industrial pollution further degrades air and water quality, impacting public health. As urbanization intensifies, sustainable development becomes essential to balance economic growth with environmental conservation. Understanding these interconnected issues is vital for implementing effective strategies that safeguard Bangladesh’s natural resources and ensure a resilient future.