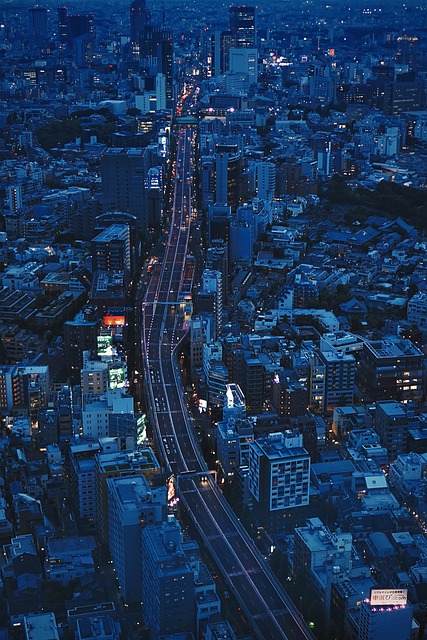
Karachi, Pakistan's economic hub, tackles air quality issues using the KDA Scheme 1 and Air Quality Index (AQI). Regular AQI updates empower residents to make informed decisions, while the scheme monitors key pollutants like PM2.5, NO2, SO2, and O3 to mitigate sources and enhance city's living conditions. Strategies include promoting sustainable transport, stricter industrial regulations, greening urban spaces, and citizen education for better environmental health.
Karachi, Pakistan’s vibrant metropolis, faces a significant challenge: air pollution. This article delves into the city’s Air Quality Index (AQI) and introduces the KDA Scheme 1, a comprehensive initiative to monitor and mitigate airborne pollutants. We explore the key metrics of this scheme, its effects on public health and the environment, and offer strategic insights for improving Karachi’s air quality. Understanding these factors is crucial for navigating the city’s complex air quality landscape.
- Karachi's Air Quality Index: An Overview
- Understanding KDA Scheme 1 Metrics
- Impact on Public Health and Environment
- Strategies for Improving Air Quality in City
Karachi's Air Quality Index: An Overview

Karachi, Pakistan’s economic hub, faces a significant challenge in maintaining healthy air quality due to its dense population and industrial activities. The Air Quality Index (AQI) serves as a critical tool for monitoring and assessing air pollution levels in the city. Scheme 1 of the KDA (Karachi Development Authority) provides a framework for understanding Karachi’s AQI, offering insights into various pollutants that contribute to poor air quality.
The index categorizes air quality based on different color codes, indicating levels of pollution: from good (green) to hazardous (red). This system allows residents and authorities alike to take necessary precautions and implement measures to mitigate pollution. Regular updates on the AQI help Karachi’s folks make informed decisions regarding outdoor activities, ensuring their well-being in this bustling metropolis.
Understanding KDA Scheme 1 Metrics

Karachi, as a bustling metropolis, faces unique challenges when it comes to air quality, leading to the implementation of the KDA Scheme 1. This initiative focuses on understanding and monitoring key metrics to ensure healthier living conditions for its residents. The scheme introduces a comprehensive set of guidelines and parameters to measure various aspects of air pollution, providing a clear picture of the city’s environmental health.
Key metrics under this scheme include particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3) levels. By regularly assessing these factors, authorities can identify sources of pollution, whether from industrial activities, vehicle emissions, or construction sites. This data-driven approach enables effective decision-making to mitigate air pollution, ultimately improving the overall quality of life in Karachi.
Impact on Public Health and Environment

The Air Quality Index (AQI) KDA Scheme 1 plays a pivotal role in monitoring and improving the air quality in Karachi, a bustling metropolis where environmental challenges are multifaceted. Poor air quality has profound implications for public health and the environment. Inhaling polluted air can lead to various respiratory issues, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature deaths, especially among vulnerable populations like children and the elderly. The environment suffers as well, with pollutants contributing to climate change, acid rain, and damage to ecosystems.
Karachi’s unique geographical location and urban dynamics exacerbate these problems. Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and open burning of waste all contribute to the city’s air pollution levels. By implementing the AQI KDA Scheme 1, authorities aim to reduce these harmful pollutants, ensuring a healthier environment for its residents. This initiative is a step towards navigating the complex web of environmental challenges, fostering a sustainable future for Karachi, and protecting the well-being of its folks.
Strategies for Improving Air Quality in City

Karachi, as a bustling metropolis, faces significant air quality challenges. However, several strategies can help improve the situation. One key approach is to promote sustainable transportation options like electric vehicles and public transit systems, which can reduce emissions from road traffic. The city can also benefit from implementing stricter industrial regulations, ensuring factories adopt cleaner production methods and adhere to emission standards.
Additionally, greening urban spaces by planting more trees and developing green infrastructure can help absorb pollutants and cool the environment. Encouraging responsible waste management practices, including recycling and proper disposal of hazardous materials, is another effective measure. Finally, raising public awareness about air quality issues and empowering citizens with knowledge on how to contribute to cleaner air can be a game-changer for Karachi’s overall environmental health.
Karachi, with its vibrant yet challenging urban landscape, faces significant air quality issues as evidenced by the city’s Air Quality Index (AQI) readings. The KDA Scheme 1 metrics provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and addressing these concerns. By recognizing the profound impact on public health and the environment, Karachi can implement effective strategies to improve air quality. Through coordinated efforts, innovative solutions, and a commitment to sustainability, the city can strive towards a cleaner, healthier future for its citizens.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.